Natural Betaine (Anhydrous): The Safer and Superior Alternative to Synthetic Additives Betaine HCl & Choline chloride in Poultry Nutrition

Dr Bhaskar Choudhary
Animal Nutritionist
Biochem Zusatzstoffe Handels- und Produktionsgesellschaft mbH
Abstract:
In the modern poultry industry, ensuring optimal health and productivity in layers, breeders, and broilers under various stress conditions is vital. Feed additives like choline chloride, synthetic betaine (anhydrous and HCl forms), and natural betaine are used to enhance performance. However, synthetic choline chloride and betaine often contain residues of ethylene oxide and trimethylamine (TMA), which pose significant risks to poultry health, including fatty liver syndrome, reproductive challenges, and respiratory hazards. The chemical synthesis of these additives highlights the adverse effects of residue contamination and explains why natural Betaine (anhydrous )(Hepatron/Beta Pro BL) is the superior choice.
1. Chemical Synthesis of Choline Chloride, Betaine, and Betaine Hcl
Choline Chloride Synthesis:
Choline chloride is produced by reacting ethylene oxide with trimethylamine, followed by neutralization with hydrochloric acid:
C2H4O + (CH3)3N + HCl —- (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OH.Cl-
Synthetic Betaine Anhydrous Synthesis:
Betaine is synthesized by methylating glycine with trimethylamine:
NH2CH2COOH + 3(CH3)3N—– (CH3)3N+CH2COO-
Betaine Hydrochloride Synthesis:
Betaine HCl is formed by reacting betaine with hydrochloric acid:
(CH3)3N+CH2COO- + HCl —– (CH3)3N+CH2COOH.Cl-
2. Risks Associated with Ethylene Oxide and Trimethylamine Residues
Ethylene Oxide (EO): permissible limit 0.2mg/g
Source: Ethylene oxide is used as a key reactant in choline chloride synthesis.
Risks and Effects:
Fatty Liver: Ethylene oxide residues exacerbate lipid accumulation in the liver, leading to fatty liver syndrome, impairing metabolism and egg production in layers.
Reproductive Challenges: In breeders, EO residues can induce oxidative damage to ovarian tissues, affecting fertility and hatchability.
Respiratory Hazards: Chronic exposure to ethylene oxide fumes or residues increases oxidative stress in respiratory tissues, leading to reduced lung function and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections.

Trimethylamine (TMA): permissible limit 10 mg/kg
Source: TMA is used as a methyl donor in the production of choline chloride and synthetic betaine.
Risks and Effects:
Fatty Liver: Excess TMA disrupts lipid metabolism by impairing the synthesis of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), leading to hepatic fat accumulation.
Reproductive Challenges: In breeders, TMA residues interfere with reproductive hormone balance, reducing fertility and chick quality.
Respiratory Hazards: Volatile TMA emissions irritate the respiratory tract, causing chronic respiratory distress in broilers and layers, especially in poorly ventilated environments.
3. Challenges of Synthetic Additives in Poultry Nutrition
Residue Toxicity: Synthetic choline chloride and betaine often leave traces of ethylene oxide and TMA, causing long-term health risks.
Liver Dysfunction: These residues impair liver detoxification and metabolic efficiency, leading to reduced productivity.
Limited Stress Resilience: Synthetic forms lack the bioactive properties of natural betaine, making them less effective in managing stress.
4. Natural Betaine (anhydrous) (Hepatron/Beta Pro BL): A Safer and More Effective Solution
Residue-Free and Safe: Hepatron/Beta Pro BL, derived from natural sources, is free of ethylene oxide and TMA residues, eliminating the associated risks of liver damage, reproductive issues, and respiratory stress.
Superior Liver Support:
– Enhances lipid metabolism, preventing fatty liver syndrome.
– Boosts detoxification pathways to handle feed-related toxins more effectively.
Enhanced Stress Management:
– Natural osmoregulatory properties stabilize cellular hydration under heat and osmotic stress.
– Promotes better feed conversion and growth performance.
5. Correlation Between Natural Betaine and Poultry Health
Fatty Liver Syndrome Prevention: Natural betaine spares choline and methionine in feed, reducing the metabolic burden on the liver and enhancing lipid transport efficiency.
Reproductive Health Support: Hepatron/BetaPro BL optimizes methylation pathways, improving ovarian function, egg production, and hatchability in breeders and layers.
Respiratory Protection: Unlike TMA-containing additives, Hepatron/Beta Pro BL improves cellular hydration and stress tolerance, protecting the respiratory tract from environmental and metabolic stress.
6. Stress in Poultry: A Multi-Faceted Challenge
Types of Stress in Poultry:
1. Environmental Stress: Heat & cold (Environment) stress in broilers & layer
2. Nutritional Stress: Imbalanced diets and mycotoxin contamination.
3. Physiological Stress: Vaccination, debeaking, and transportation.
4. Production Stress: Egg production in layers and rapid growth demands in broilers.
Role of Hepatron/Beta Pro BL in Feed application for Stress Mitigation:
Layers: Reduces egg drop during heat/Cold stress (Environment physiologica stress/ and improves shell quality.
Breeders: Enhances fertility and hatchability under environmental and nutritional stress.
Broilers: Improves growth performance and livability during transportation and heat stress.
Application of Hepatron/BetaPro BL in Drinking water: 6 hours improved water intake during treatment & outbreak condition it is advisable apart from stress mitigation what mentioned in Feed application for quick support as a clinical Nutrition
7. Why Natural Betaine (Hepatron/Beta Pro BL) is Superior
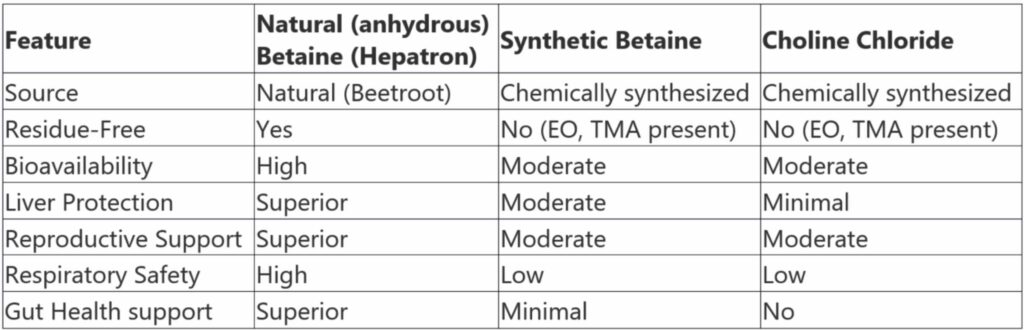
Conclusion
Residues of ethylene oxide and trimethylamine in synthetic choline chloride and betaine pose significant risks to poultry health, including fatty liver, reproductive challenges, and respiratory hazards. Natural (anhydrous )Betaine (Hepatron/Beta Pro BL) offers a safer, residue-free alternative with superior bioavailability and efficacy. By supporting liver function, improving reproductive outcomes, and protecting respiratory health, Hepatron/Beta Pro BL proves indispensable for sustainable and profitable poultry farming.
References are available on request.





